
What is assertion and when to use assertion
Assertions are primitive software engineering tool that is used in almost all programming languages. Assertions are very easy to use yet a powerful implementation-level documentation tool for developers.
Assert statements are like active comments -- they not only make assumptions clear and concise, but also if these assumptions are violated, they take some specified actions on it. Assertion is an effective way to catch program logic errors at runtime. Assertions should almost never be used to detect situations that arise during software's normal operation. For example, assertions should not be used to check for errors in a user's input.
An “assertion” is said to occur when an assertion detects that its condition is false and takes appropriate action, such as throwing an exception.
In C#, assertion is done using assert method defined in System.diagnostic debug class. Below is an example of Debug.Assert method.
int value = -1;
// If value is ever -1, then a dialog will be shown.
Debug.Assert(value == 1, "Value is -1.");
Debug.WriteLine("Value is -1");
Console.WriteLine("Value is -1");
value = 42;
// If you want to only write a line, use WriteLineIf.
Debug.WriteLineIf(value == 42, "Value is 42.");
Console.WriteLine("Value is 42");
The first assert condition is false; hence it will display the error dialog as shown below.
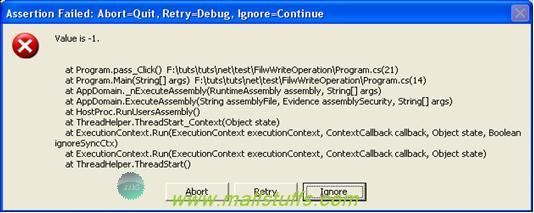
Debug statement are compiled out when project is build in Release mode. So if you run the same code in release mode, you will not see the dialog box as shown above because the compiler will ignore all the debug method statement.
Debug.WriteLine("Value is -1"); will write the string on the output window.
Debug.WriteLineIf(value == 42, "Value is 42."); will write the string on the output window if the condition is true.
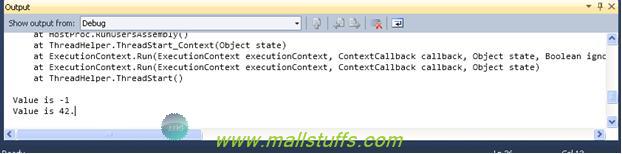
Debug.Write methods
We can also set a debug condition on the whole function. Execution of this function will depend on the attribute value set on the Conditional statement.
Let's look at an example of using assertions. This example deals with a small
[System.Diagnostics.Conditional("DEBUG")]
public static void Test(bool condition)
{
if (condition) return;
MessageBox.Show("Assertion failed.");
}
[System.Diagnostics.Conditional("DEBUG")]
public static void Test(bool condition, string message)
{
if (condition) return;
MessageBox.Show("Assertion '" + message + "' failed.");
//throw new Exception("Assertion '" + message + "' failed.");
}
The class exposes various Test methods that either accept a Boolean expression or a Boolean expression with the string message. If the Boolean value evaluates to false, we show the message in the message box.
Moreover, all the Test methods have a System.Diagnostics.Conditional attribute declared on the top of the method. This attribute ensures that a method and calls to it are only preserved in the compiled code if a particular flag was set during the compilation process. In the above code, I have chosen DEBUG as the flag, which means that calls to the Test methods only execute when the project is being debugged i.e. when the project is running in debug mode.
The above class works for both Desktop as well as ASP.NET web applications. For web applications, just ensure that you have debug="true" in the app's web.config file during development.
 here
here
Note: Images used on this website
are either a production of Bhaktivedanta Book Trust(https://www.krishna.com), Iskcon
Foundation or were found in google search under "Free to use and share". If any
of the images presented here violates copyright issues or infringes anyone copyright
or are not under "Fair use", then please bring it to our notice. Read
Disclaimer for more.
Share this to your friends. One of your friend is
waiting for your share.
Related Articles
What is assertion and when to use assertion
Post Comment